The Model of Abnormality Based on What We Can Actually Observe Is Called:
The Scientific Method
The cardinal discussion hither is that information technology is systematic meaning there is a prepare way to use it. What is that way? Well, depending on what source yous wait at information technology can include a varying number of steps:
Table : The Steps of the Scientific Method
Step | Name | Description |
0 | Inquire questions and exist willing to wonder. | To study the world effectually us you have to wonder about it. This inquisitive nature is the hallmark ofcritical thinking,or our ability to appraise claims fabricated past others and make objective judgments that are independent of emotion and anecdote and based on hard evidence, and required to exist a scientist. |
1 | Generate a enquiry question or identify a problem to investigate. | Through our wonderment well-nigh the world around us and why events occur equally they do, we begin to enquire questions that require further investigation to arrive at an answer. This investigation usually starts with aliterature review, or when we conduct a literature search through our university library or a search engine such as Google Scholar to see what questions have been investigated already and what answers have been found, so that we can identifygaps or holes in this body of work. |
2 | Attempt to explicate the phenomena we wish to study. | We now endeavor to formulate an explanation of why the event occurs as it does. This systematic explanation of a phenomenon is atheory and our specific, testable prediction is thehypothesis.We will know if our theory is right because nosotros have formulated a hypothesis which we can now test. |
iii | Test the hypothesis. | It goes without saying that if we cannot test our hypothesis, so we cannot testify whether our prediction is correct or non. Our program of action of how we will go well-nigh testing the hypothesis is called ourresearch design. In the planning stage, we volition select the appropriate research method to respond our question/test our hypothesis. |
four | Interpret the results. | With our research study washed, nosotros now examine the data to see if the blueprint we predicted exists. Nosotros need to encounter if a cause and effect statement can be made, bold our method allows for this inference. Information technology is important to know that the statistics nosotros use take on two forms. Starting time, there aredescriptive statisticswhich provide a means of summarizing or describing data, and presenting the data in a usable class. Y'all likely have heard of the mean or average, median, and fashion. Along with standard deviation and variance, these are ways to describe our information. Second, there areinferential statisticswhich let for the analysis of two or more than sets of numerical data to determine thestatistical significance of the results. Significance is an indication of how confident nosotros are that our results are due to our manipulation or pattern and not chance. |
five | Draw conclusions carefully. | Nosotros need to accurately translate our results and not overstate our findings. To exercise this, we demand to be enlightened of our biases and avoid emotional reasoning and then that they do not cloud our judgment. How then? In our effort to stop a child from engaging in cocky-injurious behavior that could cause substantial harm or even expiry, we might enlarge the success of our treatment method. |
half-dozen | Communicate our findings to the larger scientific community. | Once we have decided on whether or hypothesis was correct or not, we need to share this data with others so that they might annotate critically on our methodology, statistical analyses, and conclusions. Sharing also allows forreplication or repeating the written report to confirm its results. Communication is accomplished via scientific journals, conferences, or newsletters. |
Science has at its root three fundamental features that we will see demonstrated time and time over again throughout this text.
They are:
- Observation – In order to know virtually the world around us we have to be able to see it firsthand. When an private is affected by a mental disorder, nosotros can see it through the overt beliefs they brand. An private with depression may withdraw from activities he/she enjoys, those with social anxiety disorder will avoid social situations, people with schizophrenia may limited concern over being watched by the government, and individuals with dependent personality disorder may expect to make any determination in life until trusted others tell them what to do. In these examples, and numerous others we can suggest, the behaviors that lead us to a diagnosis of a specific disorder can easily exist observed past the clinician, the patient, and/or family and friends.
- Experimentation – To be able to makecausal or crusade and consequence statements, nosotros must isolate variables. We have to dispense one variable and see the result of doing so on another variable. Allow's say we want to know if a new treatment for bipolar disorder is as constructive equally existing treatments…or more than importantly, ameliorate. We could design a study with three groups of bipolar patients. One group would receive no handling and serve equally a control grouping. A 2d group would receive an existing and proven treatment, and would as well be considered a control group. Finally, the third group would receive the new treatment and be the experimental group. What we are manipulating is what treatment the groups go – no treatment, the older treatment, and the newer treatment. The first two groups serve as controls since we already know what to await from their results. At that place should be no change in bipolar disorder symptoms in the no treatment grouping, a general reduction in symptoms for the older handling grouping, and the same or better performance for the newer treatment group. As long as patients in the newer treatment group don't perform worse than their older handling counterparts, we can say the new drug is a success. You might wonder why nosotros would get excited nearly the functioning of the new drug being the aforementioned as the quondam drug. Does it really offer whatsoever added benefit? It terms of a reduction of symptoms, peradventure not, just it could cost less coin than the older drug and so that would be of value to patients.
- Measurement– How practise nosotros know that the new drug has worked? Merely, we can measure the person's bipolar disorders symptoms before any treatment was implemented, and and then over again in one case the treatment has ran its course. This pre-mail exam blueprint is typical in drug studies.
Types of Research Studies
The third key features called on the scientist to test his or her hypothesis. Psychology as a field of study uses v main research designs. They are:Naturalistic and laboratory observation, Clinical or Example studies, Surveys/Cocky-Report information, Correlational enquiry and Single-Case Experimental Blueprint.
Naturalistic and laboratory observation.
In terms ofnaturalistic observation, the scientist studies homo or animal behavior in its natural environs which could include the dwelling house, schoolhouse, or a forest. The researcher counts, measures, and rates behavior in a systematic way and at times uses multiple judges to ensure accuracy in how the behavior is existence measured. The advantage of this method is that you lot see behavior as information technology occurs and it is not tainted by the experimenter. The disadvantage is that it could accept a long time for the behavior to occur and if the researcher is detected and so this may influence the behavior of those being observed.Laboratory observationinvolves observing people or animals in a laboratory setting. The problem is that since the subjects know the experimenter is watching them, their behavior could get artificial.The researcher might want to know more almost parent-kid interactions and and so brings a female parent and her child into the lab to engage in preplanned tasks such equally playing with toys, eating a meal, or the mother leaving the room for a short period of time. Although laboratories are platonic for conducting such experiments, they may also exist appropriate settings for cocky-written report data in which participants answer to questionnaires. This is ideal if the researcher is seeking to collect those responses in a fixed period of fourth dimension or under atmospheric condition involving a minimum of distractions. The laboratory may likewise exist a desirable setting for investigators to ask respondents to complete self-report instruments via computer, allowing for the investigator to collect data in a systematic and uniform fashion across respondents. Clinical ascertainment is a usually employed research method to report psychopathology and we will talk almost it more throughout this form.
Clinical or Case studies

"Rat Human being" was the nickname given by Sigmund Freud to a patient whose "case history" was published in 1909. This was the second of vi case histories that Freud published, and the start in which he claimed that the patient had been cured by psychoanalysis. The nickname derives from the fact that amongst the patient's many compulsions was an obsession with nightmarish fantasies almost rats.
Psychology can also utilise a detailed description of one person or a small group based on careful observation. This was the approach the founder of psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud, took to develop his theories. The reward of this method is that you arrive at a rich description of the behavior beingness investigated but the disadvantage is that what you lot are learning may exist unrepresentative of the larger population and so lacksgeneralizability. Studying i person or a very minor group brings well-nigh the question of possibly making conclusions about all people from just one or even five or ten. The other issue is that the case study is subject to the bias of the researcher in terms of what is included in the concluding write up and what is left out. Despite these limitations, case studies can atomic number 82 us to novel ideas about the crusade of abnormal beliefs and aid united states of america to study unusual weather condition that occur too infrequently to study with large sample sizes and in a systematic mode. The case report can provide detailed descriptions of specific and rare cases.The major disadvantages of the case study in psychology is the inability to draw cause and upshot relationships or examination hypotheses, and researchers thereby, must be extremely precise in their methods and, equally much equally possible, take an objective and unbiased approach. They are likely to seek publication in a journal that specializes in the case report arroyo rather than one that relies on large sample or experimental data.
Since the 1980'due south a broad telescopic of case study approaches accept developed. This range accentuates the flexibility of case study enquiry as a distinct course of inquiry that enables comprehensive and in-depth insight into a various range of issues across a number of disciplines. While differences exist in some areas, commonalities are axiomatic that can guide the application of a case report enquiry design. Central contributors to the development of case study agree that the focus of a case study is the detailed inquiry of a unit of assay every bit a bounded organisation (the instance), over time, within its context. With the capacity to tailor approaches, case study designs can address a wide range of questions that inquire the why, what, and how of an effect and assistance researchers to explore, explicate, draw, evaluate, and theorize nigh complex issues in context. Outcomes can pb to an in-depth understanding of behaviors, processes, practices, and relationships in context. Ongoing awarding of and audio debate about the value, validity, and capability of example study research have strengthened the efficacy of instance report approaches as powerful forms of qualitative research.
Surveys/Self-Report data
Survey research is a quantitative and qualitative method with two important characteristics. Beginning, the variables of interest are measured using self-reports (using questionnaires or interviews). In essence, survey researchers ask their participants (who are often called respondents in survey research) to report directly on their own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. 2d, considerable attention is paid to the issue of sampling. In detail, survey researchers have a strong preference for large random samples considering they provide the almost authentic estimates of what is true in the population. In fact, survey research may exist the only arroyo in psychology in which random sampling is routinely used. Beyond these two characteristics, almost annihilation goes in survey enquiry. Surveys can be long or curt. They tin exist conducted in person, by telephone, through the postal service, or over the Internet. They tin be about voting intentions, consumer preferences, social attitudes, health, or anything else that information technology is possible to ask people almost and receive meaningful answers. Although survey data are often analyzed using statistics, there are many questions that lend themselves to more qualitative analysis.
Surveys allow for the collection of big amounts of information rapidly only the actual survey could exist boring for the participant andsocial desirability, when a participant answers questions dishonestly and so that he/she is seen in a more favorable light, could be an issue. Y'all could alternatively gather this information via an interview in a structured or unstructured fashion. Virtually survey research is non-experimental. It is used to describe single variables (due east.g., the prevalence of schizophrenia in the general population, etc.) and also to assess statistical relationships between variables (east.g., the relationship betwixt income and mental health).Researchers also use surveys to gather statistics well-nigh the frequency of psychological symptoms. For example, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Assistants of the U.Southward. government (SAMHSA) conducts a yearly National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH).

NSDUH measures: utilize of illegal drugs, prescription drugs, alcohol, and tobacco and misuse of prescription drugs ; substance use disorder and substance utilise; treatment major depressive episode and low care; serious psychological distress, mental affliction, and mental health care
In the study of psychopathology, some of the most important survey data we will rely on comes from large-calibration epidemiological studies. This is how we know how many people are probable to develop a disorder, and who peculiarly is at risk. The type of information nosotros use for these purposes falls into ii categories: (ane) The prevalence of a disorder refers to the number of people who have ever had the disorder over a specified catamenia of time and (two) The incidence of a disorder is the frequency of new cases of a disorder within a given time period. Both are calculated for the population as a whole and for detail segments of the population past sex, age group, geographic region, or social class, for case.
Advantages of surveys
The advantages of survey techniques include:
- Information technology is an efficient manner of collecting information from a large number of respondents. Very large samples are possible. Statistical techniques tin can be used to decide validity, reliability, and statistical significance.
- Surveys are flexible in the sense that a wide range of information tin be collected. They tin can be used to written report attitudes, values, beliefs, and past behaviors.
- Because they are standardized, they are relatively gratis from several types of errors.
- They are relatively easy to administer.
- At that place is an economy in data collection due to the focus provided by standardized questions. Only questions of interest to the researcher are asked, recorded, codified, and analyzed. Time and money is non spent on tangential questions.
Disadvantages of surveys
Disadvantages of survey techniques include:
- They depend on subjects' motivation, honesty, memory, and power to respond. Subjects may not exist aware of their reasons for any given action. They may accept forgotten their reasons. They may not be motivated to give accurate answers, in fact, they may be motivated to give answers that nowadays themselves in a favorable calorie-free.
- Surveys are not appropriate for studying complex social phenomena. The individual is not the best unit of analysis in these cases. Surveys do not give a total sense of social processes and the analysis seems superficial.
- Structured surveys, particularly those with closed ended questions, may accept low validity when researching affective variables.
- Survey samples are usually self-selected, and therefore non-probability samples from which the characteristics of the population sampled cannot exist inferred.
Correlational research
This inquiry method examines the relationship between 2 variables or two groups of variables. A numerical measure of the forcefulness of this human relationship is derived, called the correlation coefficient , and tin range from -one.00, a perfect changed relationship meaning that as one variable goes up the other goes downwardly, to 0 or no relationship at all, to +one.00 or a perfect relationship in which equally one variable goes upward or down and so does the other. In terms of a negative correlation we might say that every bit a parent becomes more rigid, controlling, and cold, the attachment of the child to parent goes down. In contrast, every bit a parent becomes warmer, more loving, and provides structure, the child becomes more than fastened. Correlations are useful considering they can indicate a predictive human relationship that tin be exploited in practice. The advantage of correlational research is that you can correlate annihilation. The disadvantage is that you lot can correlate annihilation. Variables that really exercise not have any relationship to i some other could be viewed as related. Yes. This is both an advantage and a disadvantage. For instance, we might correlate instances of making peanut butter and jelly sandwiches with someone we are attracted to sitting almost us at lunch. Are the two related? Not likely, unless you brand a really adept PB&J but and so the person is probably just interested in y'all for nutrient and not companionship. The main upshot here is that correlationdoes non allow you to make a causal statement. The phrase "correlation does non imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect human relationship betwixt two variables solely on the footing of an observed clan or correlation betwixt them.
A special from of correlational research is theepidemiological study, a study that compares 2 groups of people who are akin except for one factor, such as exposure to a chemical or the presence of a health effect; the investigators try to determine if any cistron is associated with the health effect. In psychological research, the prevalence and incidence of a disorder in a specific population are measured. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, manual, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such equally in clinical trials.
Experiments

Harry Frederick Harlow (Oct 31, 1905 – December 6, 1981) was an American psychologist all-time known for his maternal-separation, dependency needs, and social isolation experiments on rhesus monkeys, which manifested the importance of caregiving and companionship to social and cerebral evolution.
This is a controlled exam of a hypothesis in which a researcher manipulates one variable and measures its effect on another variable. The variable that is manipulated is called theindependent variable (IV)and the one that is measured is called thedependent variable (DV). In the example above, the treatment for bipolar disorder was the Iv while the bodily intensity or number of symptoms serves as the DV. A mutual feature of experiments is to have acontrol groupthat does not receive the handling or is non manipulated and anexperimental groupthat does receive the treatment or manipulation. If the experiment includesrandom consignment participants have an equal chance of being placed in the control or experimental grouping. The control group allows the researcher (or teacher) to make acomparing to the experimental group, make our causal statement possible, and stronger. In our experiment, the new treatment should show a marked reduction in the intensity of bipolar symptoms compared to the group receiving no handling, and perform either at the same level every bit, or better than, the older treatment. This would be the hypothesis we begin the experiment with.
In research on the causes of abnormal behavior, it may be difficult to fix a truthful experimental written report. Many of the variables that are of most interest to psychologists are ones that the investigator cannot control; hence, they are not truly "independent." For instance, bipolar disorder can never be an contained variable because the researcher cannot manipulate it. Similarly, researchers cannot randomly assign people to groups based on their biological sex. Studies that investigate differences amid groups not adamant by random assignment are known as "quasi-experimental."
The gold standard for research in clinical psychology is the randomized controlled trial (RCT) , in which researchers randomly assign participants to conditions in which they receive unlike forms of intervention. Otherwise, a Randomized controlled trial: (RCT) is a study in which people are allocated at random (by chance alone) to receive one of several clinical interventions. One of these interventions is the standard of comparing or command. The command may be a standard exercise, a placebo ("carbohydrate pill"), or no intervention at all. The key to this method is the use of randomization, which minimizes the chances that bias can enter into the decision of which participants receive which treatment. Because this is such a powerful design, RCT is used every bit the foundation for evidence-based treatment , in which clients receive interventions based on the findings of controlled clinical studies.
There are times when nosotros begin a drug study and to ensure participant expectations have no consequence on the last results through giving the researcher what he/she is looking for. Across the RCT blueprint, well-controlled research in clinical psychology has a placebo condition in which participants receive a treatment similar to the experimental treatment, but one that lacks the key characteristic of the treatment of involvement. If the study is evaluating effectiveness of medication (in our instance, symptoms improve whether or not a treatment is given or not), the placebo would have inert ingredients or a sugar pill made to expect exactly like the pill given to the experimental group. If participants are randomly assigned to placebo versus treatment, the design is referred to as a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial . This way, participants all are given something, simply cannot figure out what exactly information technology is. You might say this keeps them honest and allows the results to speak for themselves.
In studies evaluating effectiveness of therapy, scientists must pattern the placebo in a mode that mimics, but is not the same as, the actual therapy. Ideally, researchers would want the placebo participants to receive treatments of the aforementioned frequency and duration as the experimental grouping participants who are receiving psychotherapy.
Expectations about the experiment's outcome can touch on both the investigator and the participant. These then-chosen "demand characteristics" tin can compromise the conclusions about the intervention's true effectiveness. Obviously, the investigator should be as unbiased equally possible, only there still may exist subtle means that he or she communicates cues that bear upon the participant'due south response. The participant may too have a personal agenda in trying to prove or disprove the study's supposed true intent. The best way to eliminate need characteristics is to utilize a double-blind method, which shields both investigator and participant from knowing either the written report'south purpose or the nature of the patient's treatment. Thus, a double–blind, placebo–controlled clinical trial is a medical study involving human being participants in which neither side knows who's getting what handling and placebo are given to a control group.
In studies involving medication, a completely inert placebo may not be sufficient to establish true experimental control. If the researchers know that a medication produces dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, or upset tum, and then the placebo must also mimic these side furnishings or participants will know they are receiving placebos. We might so consider the "active placebo" condition. An active placebo is a drug that has no upshot on the symptom under investigation, but that mimics the side effects of the active treatment. Withal, the hypothesis that side furnishings can enhance the placebo outcome has not been subjected to an experimental test.
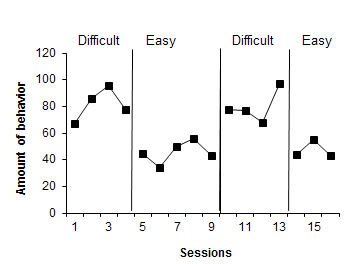
An case of an ABAB research design to examination the effects of easy versus hard school piece of work on the off-task beliefs with one kid.
Finally, the study of mental disease does non always afford us a large sample of participants to written report and and then nosotros have to focus on one private. This is called aunmarried-subject experimental designand differs from a example written report in the sheer number of strategies that tin can exist used to reduce potentialconfounding variables, or variables not originally part of the inquiry blueprint but contribute to the results in a meaningful way. One type of single-subject experimental design is thereversal orABAB design. Kuttler, Myles, and Carson (1998) used social stories to reduce tantrum behavior in two social environments in a 12-year old student diagnosed with autism, Frail-X syndrome, and intermittent explosive disorder. Using an ABAB pattern, they plant that precursors to tantrum behavior decreased when the social stories were available (B) and increased when the intervention was withdrawn (A). A more than recent study (Balakrishnan & Alias, 2017) too established the utility of social stories every bit a social learning tool for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using an ABAB design. Four students were included in the study and during the baseline phase (A) they were observed and data recorded on an observation form. During the treatment phase (B), they were read the social story and data recorded in the same manner. Upon completion of the first B, the student was returned to A which was followed one more than time by B and the reading of the social story. In one case the second handling stage concluded, the participation was monitored once again to obtain a final outcome. All students showed improvement during the handling phases in terms of the number of positive peer interactions they had and and then dropped back down in terms of the number of such interactions. From this the researchers concluded that the social story led to the increase in positive peer interactions of children with ASD.
Multi-method enquiry.As you lot have seen above, no single method lonely is perfect. All have their strengths and limitations. Equally such, for the psychologist to provide the most clear movie of what is affecting behavior or mental processes, several of these approaches are typically employed at different stages of the inquiry written report. This is calledmulti-method research.
Research in Behavioral Genetics
Human Behavior Genetics is an area of psychological study that looks at the genetic component that underlies human behavior. For case, some people are born with a nervous disposition, or an easy-going personality, and this bones in-built-in personality style influences their manner of reaction to stress and challenges. Information technology is substantially the study of the 'nature vs, nurture' debate. The goal in behavioral genetic research is to identify which behaviors are influenced by genes and which are mostly influenced by the environment and situational factors. This field studies the connections between genes and behavior. Twin studies are usually used. Twin Studies is a inquiry design that studies the differences betwixt nature and nurture in individual psychology. By observing the differences between twins, both identical and fraternal, it is theorized that a distinction between behaviors; mental patterns, tastes. likes an dislikes, etc. that are inborn (genetic) or learned can be made. The Minnesota Report of Twins Reared Apart—a well-known study of the genetic basis for personality—conducted enquiry with twins from 1979 to 1999. Adoption studies are 1 of the classic tools of behavioral genetics. These studies are used to estimate the degree to which variation in a trait is due to ecology and genetic influences. Adoption studies are typically used together with twin studies when estimating heritability.
The beginning adoption study on schizophrenia published in 1966 past Leonard Heston demonstrated that the biological children of schizophrenic parents were just as likely to develop schizophrenia whether they were reared past the parents or adopted and was essential in establishing schizophrenia as genetic instead of being a effect of kid rearing methods. This discovery was washed through a process of interviews of both a child that was adopted along with their biological mother who independent the schizophrenia gene, and of adopted child along with their female parent who did non contain the schizophrenia gene. The experiment was conducted more in one case on various families and connected resulting on the schizophrenia kid inheriting the gene from his mother. This supports the theory that it doesn't matter what specific environs a child is raised in; if its parent or parents endure from a mental disorder, the risk for suffering from the same disorder will exist equal regardless of if the child was raised with its biological parents or with its adoptive parents (Plomin et al., 1997).Like studies that followed have shown that mental disorders such as alcoholism, hating behavior, depression and schizophrenia take a large genetic component that interacts with environmental risk factors such equally family conflict, poor cohesion and deviant advice. Recent studies has shown that childhood disorders are not only genetic, merely form in more children that are adopted vs children that are not adopted. Many researchers of this topic believed the disorder developed over the fourth dimension the child was adopted. With further research being done, results have shown that some of the adoptees had been already diagnosed with the disorder before they were even adopted. Researchers concluded the disorders are caused by the fashion a child is raised and also from the genes of their birth parents. The other few may accept developed the disorders later beingness adopted due to marvel and trouble finding their true identity. Parents that are willing to adopt are always advised to exist aware of the phenomenon that a child that is to be adopted may demand aid on dealing with psychological issues.
Cross-fostering tin be used to study the affect of postnatal environment on genetic-linked diseases equally well as on behavioral pattern. In behavioral studies, if cross-fostered offspring show a behavioral trait like to their biological parents and unlike from their foster parents, a beliefs can be shown to take a genetic basis. Similarly if the offspring develops traits different to their biological parents and similar to their foster parents environmental factors are shown to be ascendant. In many cases there is a blend of the two, which shows both genes and environment play a part. Studies of children in foster care have shown that alcoholism is both genetic and environmental: early onset alcoholism can be linked to biological parentage, whereas adult onset alcoholism is often influenced by the alcohol abuse by foster parents.
More precise methods of behavioral genetics take advantage of new methods of genetic testing. In gene mapping , researchers examine and connect variations in chromosomes to functioning on psychological tests or diagnosis of specific disorders. Molecular genetics studies how genes translate hereditary data into the instructions the genes give to the manufacturing of proteins in the cell.
These newer methods in the written report of abnormal psychology are providing a rapidly expanding literature to help us sympathise the interplay betwixt people's genetic makeup (biological science), mental health and beliefs (psychology), and sociocultural environment (social globe) that determine the class of their health-related outcomes. It is hoped that this field will requite researchers insight into the biological causes, and ultimately treatment, of many of the most serious and troubling psychological disorders that until now have been fully understood.
Serious Science – http://serious-science.org
Behavioral geneticist Robert Plomin on twin studies, genetic influence of parents on their children, and i% of DNA that makes people different
Tradeoffs in Inquiry
Even though in that location are serious limitations to correlational and quasi-experimental research, they are non poor cousins to experiments and longitudinal designs. In addition to selecting a method that is appropriate to the question, many applied concerns may influence the determination to employ one method over another. Ane of these factors is simply resource availability—how much time and money do yous accept to invest in the inquiry? Oft, we survey people even though it would exist more precise—simply much more hard—to rails them longitudinally. Peculiarly in the case of exploratory inquiry, information technology may make sense to opt for a cheaper and faster method first. And so, if results from the initial study are promising, the researcher can follow up with a more than intensive method.
Beyond these practical concerns, some other consideration in selecting a research pattern is the ethics of the written report. For example, in cases of brain injury or other neurological abnormalities, it would be unethical for researchers to inflict these impairments on healthy participants. Nonetheless, studying people with these injuries tin can provide nifty insight into human psychology (eastward.g., if nosotros larn that harm to a detail region of the brain interferes with emotions, we may exist able to develop treatments for emotional irregularities). In addition to brain injuries, there are numerous other areas of research that could be useful in agreement the human mind but which pose challenges to a truthful experimental design—such as the experiences of state of war, long-term isolation, abusive parenting, or prolonged drug employ. All the same, none of these are conditions nosotros could ethically experimentally manipulate and randomly assign people to. Therefore, ethical considerations are another crucial factor in determining an appropriate research design.
Research Methods: Why Y'all Need Them
But look at any major news outlet and you'll observe research routinely beingness reported. Sometimes the journalist understands the inquiry methodology, sometimes non (east.thousand., correlational prove is often incorrectly represented as causal testify). Frequently, the media are quick to describe a decision for yous. Afterwards reading this module, you should recognize that the strength of a scientific finding lies in the strength of its methodology. Therefore, in order to be a savvy consumer of research, you need to sympathise the pros and cons of unlike methods and the distinctions among them. Plus, understanding how psychologists systematically go about answering enquiry questions volition assistance you to solve issues in other domains, both personal and professional, not just in psychology.
Key Takeaways
ABAB Inquiry Design
A single participant experiment where the A phase consists of a series of sessions where no consequences following a specific behavior occurs and in B phase consists of a series of sessions where the consequence is provided following each occurrence of that beliefs. These phases are alternated in an ABAB fashion to rule out confounding variables or alternative explanations for the findings.
Confounds
Factors that undermine the ability to draw causal inferences from an experiment.
Correlation
Measures the association between two variables, or how they become together.
Dependent variable
The variable the researcher measures merely does not manipulate in an experiment.
Experimenter expectations
When the experimenter'south expectations influence the outcome of a study.
Independent variable
The variable the researcher manipulates and controls in an experiment.
Longitudinal study
A written report that follows the same grouping of individuals over time.
Operational definitions
How researchers specifically mensurate a concept.
Participant demand
When participants behave in a manner that they retrieve the experimenter wants them to behave.
Placebo effect
When receiving special handling or something new affects human being beliefs.
Quasi-experimental design
An experiment that does not require random assignment to conditions.
Random assignment
Assigning participants to receive unlike conditions of an experiment past chance.
Respondents
Participants in survey research who are asked to report directly on their ain thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Survey research
A quantitative and qualitative method with 2 of import characteristics; variables are measured using self-reports and considerable attention is paid to the issue of sampling.
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/hvcc-abnormalpsychology/chapter/1-6-research-methods-in-abnormal-psychology/
0 Response to "The Model of Abnormality Based on What We Can Actually Observe Is Called:"
Post a Comment